Describe the Process of Blood Clotting Ib Biology
Clotting can prevent us from bleeding to death and protect us from the entry of bacteria and viruses. Prevent excessive blood loss from the body when there is a damage of the blood vessel.
After the complete repair of the damaged region the clot is dissolved by an enzyme Plasmin.

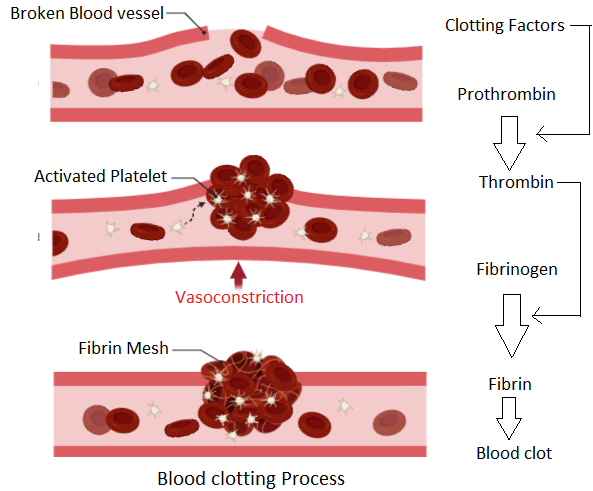
. Necessity for blood clotting. Blood flow to the area increases If a blood vessel has been ruptured Blood clotting must be activated. Prothrombin activated to thrombin.
Mesh of fibrinfibres seals woundtraps plateletsred blood cells. The Blood Coagulation definition states that the Blood clotting mechanism is the process through which a thrombus or clot is formed which restricts excess Blood from flowing out. Clotting haemostasis is the mechanism by which broken blood vessels are repaired when damaged.
Platelets come into contact with an area of an artery wall which has become damaged changing their shape from flattened disks to long thin projections. When you have a bleeding disorder youre unable to. Blood clotting IB Biology.
Blood plasma contains soluble fibrinogen. The damaged tissue and platelets release chemicals known as clotting factors that convert prothrombin into thrombin. The fibre mesh traps red blood cells white blood cells and platelets eventually forming a blood clot.
Blood vessel spasm the formation of the platelet plug and the blood clot formation process. 1111 Describe the process of blood clotting. Clotting factors together with calcium ions and vitamin k make it possible for prothrombin to become thrombin.
The blood clotting process is a multistep activity known as coagulation. The platelets stick together forming a temporary plug. The function of a blood clot is to prevent blood loss from damaged blood vessels.
When the entire coagulation process works properly blood holds firmly together at the site of an injury and bleeding stops. TAP THE CARD TO FLIP IT. There are two key components of a blood clot platelets and insoluble fibrin strands.
Prevent excessive blood loss from the body when there is a damage of the blood vessel. Its vital that blood clots when we have a surface injury that breaks blood vessels. Blood clotting or coagulation is a biological process that stops bleeding.
Fibrin forms a mesh of fibres across wounds. Maintain the blood pressure. The clotting process begins with the release of clotting factors either from damaged tissue cells or from platelets.
Known as blood coagulation. Fibrin strands form a net that entraps more platelets and other blood cells red cells and white cells producing a clot that plugs the break. Initial rapid localised response a tissue makes when it has been damaged.
Prothrombin is converted to the active enzyme thrombin. Clotting factors cause the production of thrombin. Describe the blood clotting cascade including the role of platelets clotting factors thrombin fibrinogen and fibrin.
Fibrin makes a mesh-like structure around the platelet plug made initially and the blood cells are trapped in this mesh to form a clot. Fibrinogenfibrin which captures red blood cells. Forming a clot prevents blood loss entry of bacteriapathogens.
In order for a blood clot to form activated platelets and the damaged tissue release clotting factors which are proteins in the blood that control bleeding. Soluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin. The blood clotting process or coagulation is an important process that prevents excessive building in case the blood vessel becomes injured.
Thrombin catalyses the conversion of soluble fibrinogen into the fibrous protein fibrin. Damaged blood cells release chemicals that stimulate platelets to adhere to the damaged areaThis forms a plug. Causes and consequences of blood clot formation IB Bio 2015.
CLICK THE CARD TO FLIP IT. The immediate process of stopping bleeding after injury is known as hemostasis and involves three events which are. The Extrinsic pathway and Intrinsic pathway leads to a common pathway The clotting factors convert the clotting protein proth rombin to.
Cascade of reactionsseries of stages prevent accidental clottingspeed up clotting. Thrombin makes fibrinogen is soluble become fibrin not soluble which forms a mesh of fibres. Maintain the blood pressure.
The Blood clotting mechanism has various steps that finally result in Blood Coagulation. Up to 24 cash back Fibrin strands form a net that entraps more platelets and other blood cells red cells and white cells producing a clot that plugs the break. Clotting factor released by plateletsdamaged tissuecells.
Topic 11 Human Health and Physiology 2 1111 Describe the process of blood clotting Blood clots to prevent too much blood loss and prevent pathogens from entering the body Some plasma proteins are involved in clotting such as prothrombin and fibrinogen Platelets form in bone marrow along with red cells erythrocytes and white cells leucocytes. Forms a net of fibres trapping blood cells. This gel-like mass is created from fibrin and platelets.
Prevent the entry of microorganism and foreign particles into the body. Describe the blood clotting process. The clotting factors then catalyse the reaction of the inactive zymogen prothrombin to the active form known as thrombin.
Clots also form inside our body when a blood vessel is injured. Clotting of the blood occurs only when thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin clot. Platelets and damaged cells release clotting factors.
Fibrinogen converted into fibrin. Thromboplastin released from damaged tissue and platelets as well as Ca2 and vitamin K from the plasma are released which. Enzyme thrombin catalyzes the conversion of soluble plasma proteins fibrinogen into insoluble fibrous protein fibrin.
Clotting functions to prevent blood loss from the body and limit pathogenic access to the bloodstream when the skin is broken.

Blood Clotting Ib Biology Youtube
Briefly Describe The Stages In The Clotting Of Blo Class 11 Biology Cbse

Comments
Post a Comment